Rail thermite welding material
- Description
- Inquiry
Rail thermite welding material also known as exothermic welding or aluminothermic welding, is a process that uses the intense heat generated from a chemical reaction to weld railroad tracks together. The material used in this process is a thermite composition, which typically includes:

Rail thermite welding material
Aluminum Powder: This is the fuel for the reaction. Aluminum is a highly reactive metal that, when finely powdered, reacts exothermically with metal oxides.
Iron(III) Oxide (Fe2O3): This serves as the oxidizer in the reaction. When combined with aluminum powder, it reacts to produce molten iron and aluminum oxide, along with a great deal of heat.
The basic chemical reaction in thermite welding is as follows:
[ Fe_2O_3 + 2 Al \rightarrow 2 Fe + Al_2O_3 + Heat ]
This reaction is known as a reduction-oxidation reaction (redox reaction) where aluminum reduces the iron oxide to iron, and in doing so, gets oxidized to aluminum oxide. The reaction is highly exothermic, meaning it releases a significant amount of heat, enough to melt the iron.
In the context of rail welding, the molten iron produced by the thermite reaction is what fuses the rail ends together. The process involves the following steps:
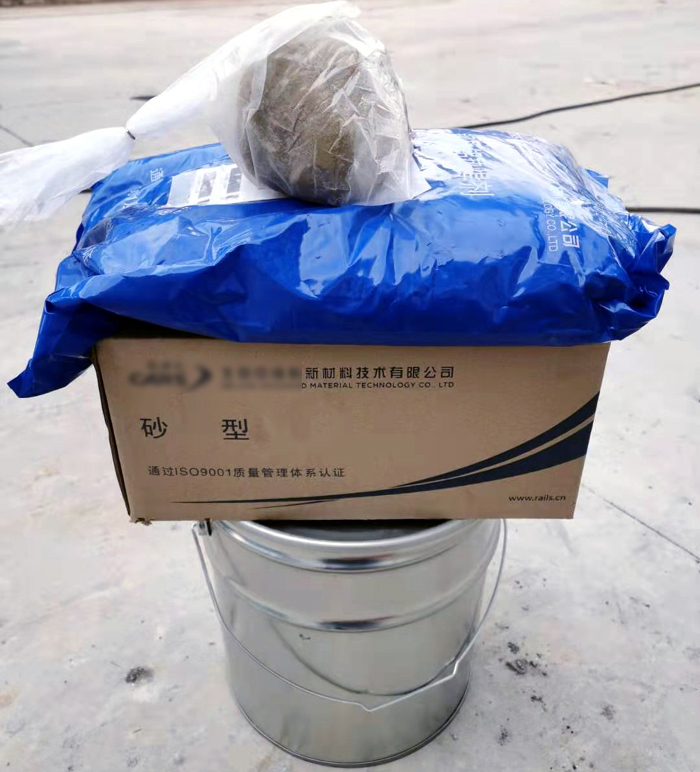
Preparation: The ends of the rails to be joined are cleaned and aligned. A mold, known as a crucible, is placed around the joint to contain the molten iron.
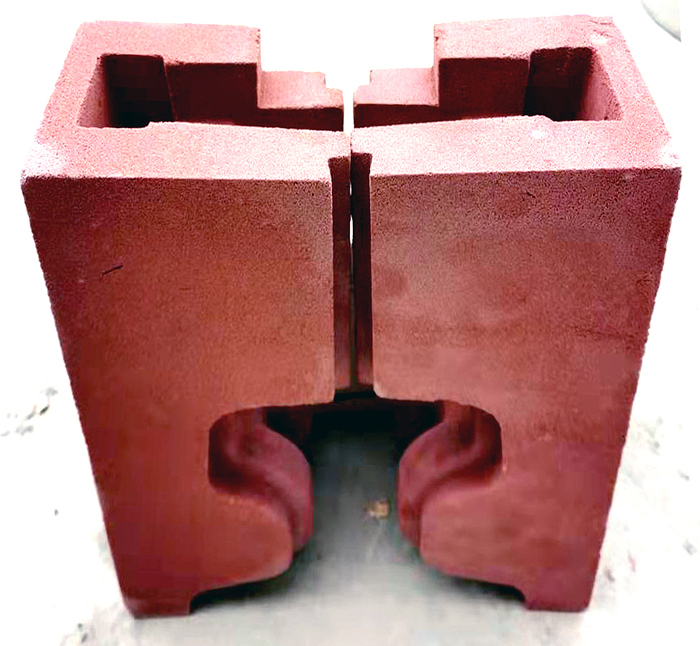
Rail thermite welding material mould
Ignition: The thermite mixture is placed in the crucible and ignited, usually with a flammable primer or a sparkler-like igniter.
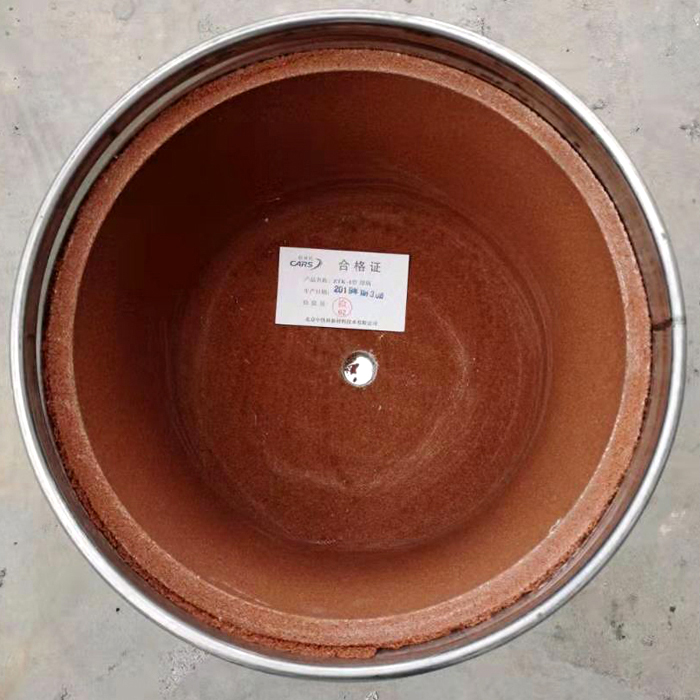

Rail thermite welding material crucible

Rail thermite welding material mould of rail

Rail thermite welding material combustion rod
Reaction: The thermite mixture reacts, producing molten iron which flows into the gap between the rail ends.
Solidification: The molten iron solidifies to form a solid weld, fusing the rail ends together.
Finishing: After cooling, excess material is removed, and the weld is ground down to ensure a smooth, continuous rail surface.
Thermite welding is often preferred for rail applications because it produces a high-quality weld that is strong and durable, capable of withstanding the heavy loads and stresses associated with rail traffic. It also has the advantage of being portable and relatively easy to perform in the field, which is essential for repairing and maintaining railway tracks.
We can make mould to weld below steel rails:
If you need it, please feel free to contact us.