Railway tracks are an essential component of China’s railway transportation system. Among the various types of tracks used, three prominent ones are heavy rail, light rail, and lifting rail. These tracks differ primarily in terms of the weight and purpose of the steel rails.
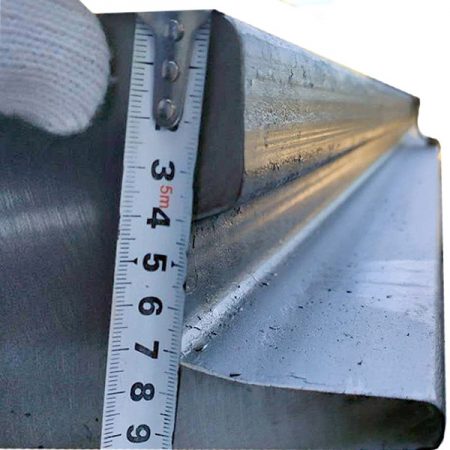
Heavy rail and light rail are distinguished by the weight of the steel rail per unit length. Steel rails that weigh more than 38kg per meter are classified as heavy rails, while those weighing less than 30kg per meter fall into the category of light rails. Heavy rails can further be categorized into general railway heavy rails and lifting rails based on their specific applications. Generally, heavy rails are predominantly utilized on railway tracks, while lifting rails find their primary use as guide rails for cranes. A visual examination of the cross-section of these tracks reveals slight differences in their shapes. Lifting rails are shorter in height, wider in width, and possess a thicker waist, whereas railway heavy rails exhibit the opposite characteristics.
It is important to note that heavy rail differs from light rail not only in terms of the weight of the track itself but also in the type of vehicles that travel upon it. Heavy rail serves as the track for robust and weighty vehicles, necessitating specifications that can support the increased load. Consequently, heavy rails are thicker and thus heavier, demanding higher standards for the steel rail construction.
In contrast, light rail accommodates lighter vehicles and possesses rail tracks that are lighter in weight. This enables them to operate efficiently while maintaining appropriate safety standards. Light rail systems are often employed in urban areas for passenger transportation, connecting various parts of the city with a focus on convenience and accessibility.
Lifting rail, as the name suggests, finds its main application in crane operations. The design of lifting rails accounts for the unique requirements of crane systems, providing stability, durability, and the capability to withstand heavy loads. These rails are specifically engineered to support the movement of cranes along their designated paths, ensuring efficient and safe lifting operations in industrial settings.
The diverse range of rail types available in China’s railway network reflects the specific demands of different transportation scenarios. Heavy rail, light rail, and lifting rail each serve distinct purposes, catering to the needs of heavy vehicles, urban passenger transportation, and crane operations, respectively. By leveraging these specialized tracks, China’s railway transportation system can effectively support various industries and facilitate the smooth movement of goods and people across the country.
We can supply the international standard steel rails as below:
If you need anyone, please feel free to contact us.